5 Missing data sensitivity analysis
This document contains a missing data sensitivity analysis.
We first load the required packages.
knitr::opts_chunk$set(cache = TRUE)
library(lavaan)
library(brms)
library(patchwork)
library(tidyverse)
library(bayestestR)
library(multidplyr)
library(here)
library(knitr)
library(mice)
# mcmc setup
options(mc.cores = 1)
if (require("cmdstanr")) options(brms.backend = "cmdstanr")
ITER <- 2000
WARMUP <- 1000
# imputation
# different delta values
deltas <- c(2, 1, 0, -1, -2)
## number of imputations
m <- 20For the sensitivity analysis we keep only Affect and Hours.
d_riclpm_wide <- read_rds(here("Temp", "d_riclpm_wide.rds"))
# keep only necessary vars
d <- filter(d_riclpm_wide, y_var == "Affect", x_var == "Hours")5.1 Imputation model
We use MICE to impute a missing not a random (MNAR) mechanism using delta adjustment. Predictive mean matching (PMM) is used for the actual imputations.
#' Perform imputation using MICE
#'
#' @param data the data
#' @param delta delta adjustement; a constant that's removed from the MAR imputation
#' @param m number of imputations
#'
#' @return a mice imputation object
mice_mnar_delta <- function(data, delta = 0, m = 5) {
d2 <- data[, !names(data) %in% c("pid", "y_var", "x_var")]
pred <- make.predictorMatrix(d2)
imp0 <- mice(
d2,
print = FALSE,
pred = pred,
m = 1
)
# pred <- quickpred(d2, minpuc = 0.33)
# do not impute hours
pred[, "x1"] <- 0
pred[, "x2"] <- 0
pred[, "x3"] <- 0
post <- imp0$post
method <- imp0$method
method[names(method) %in% c("x1", "x2", "x3")] <- ""
# delta adjustment
# squeeze to scale range
cmd <- paste("imp[[j]][,i] <- squeeze(imp[[j]][,i] +", delta, ", c(-6, 6))")
post[c("y1", "y2", "y3")] <- cmd
imp <- mice(
d2,
print = FALSE,
pred = pred,
post = post,
method = method,
m = m
)
imp
}Here we inspect the imputations, by creating density plots of observed and imputed values for delta = 0 and -2.
imp2 <- mice_mnar_delta(data = d, delta = -2, m = m)
imp_mar <- mice_mnar_delta(data = d, delta = 0, m = m)
densityplot(imp_mar, ~ y1 + y2 + y3)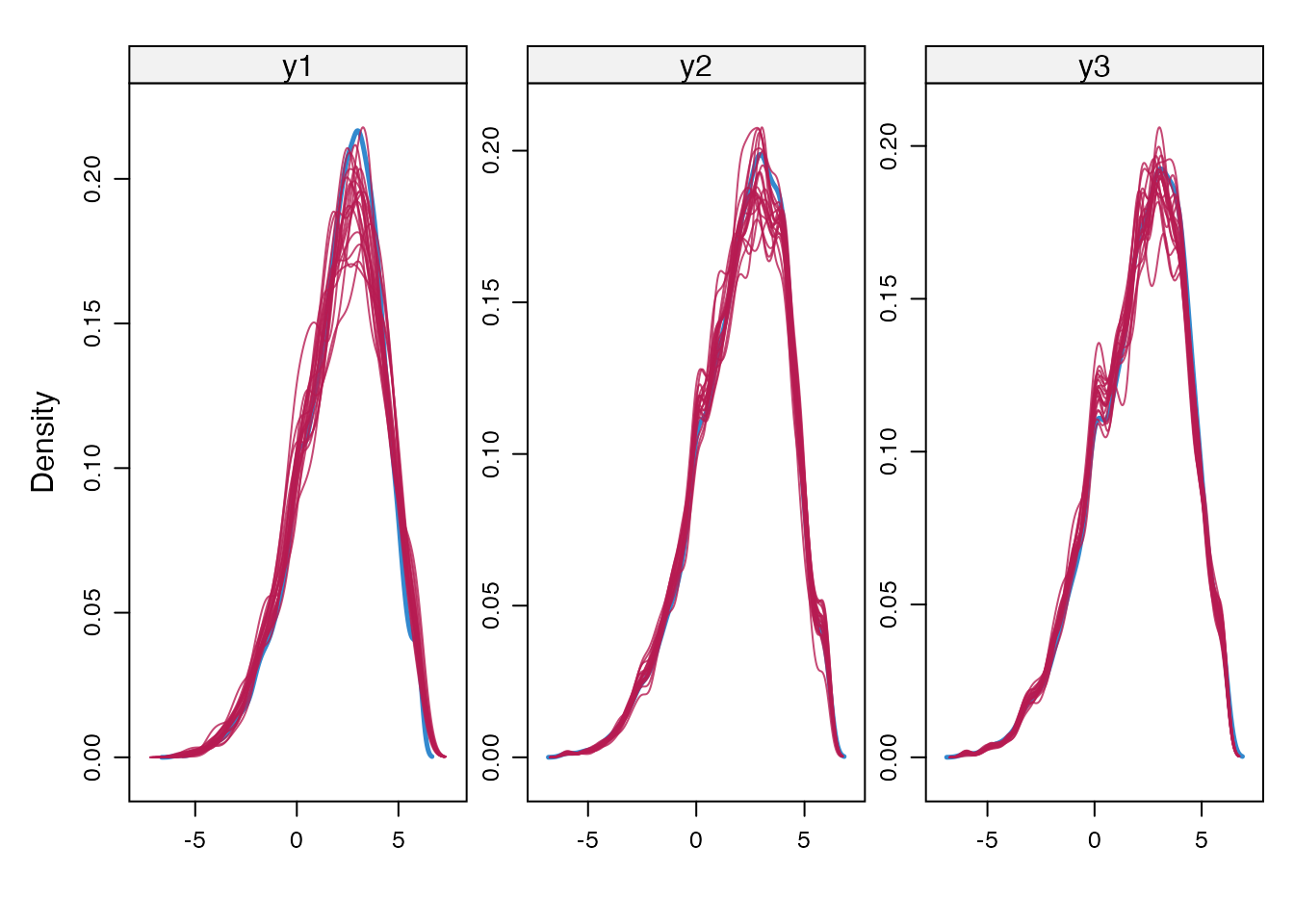
densityplot(imp2, ~ y1 + y2 + y3)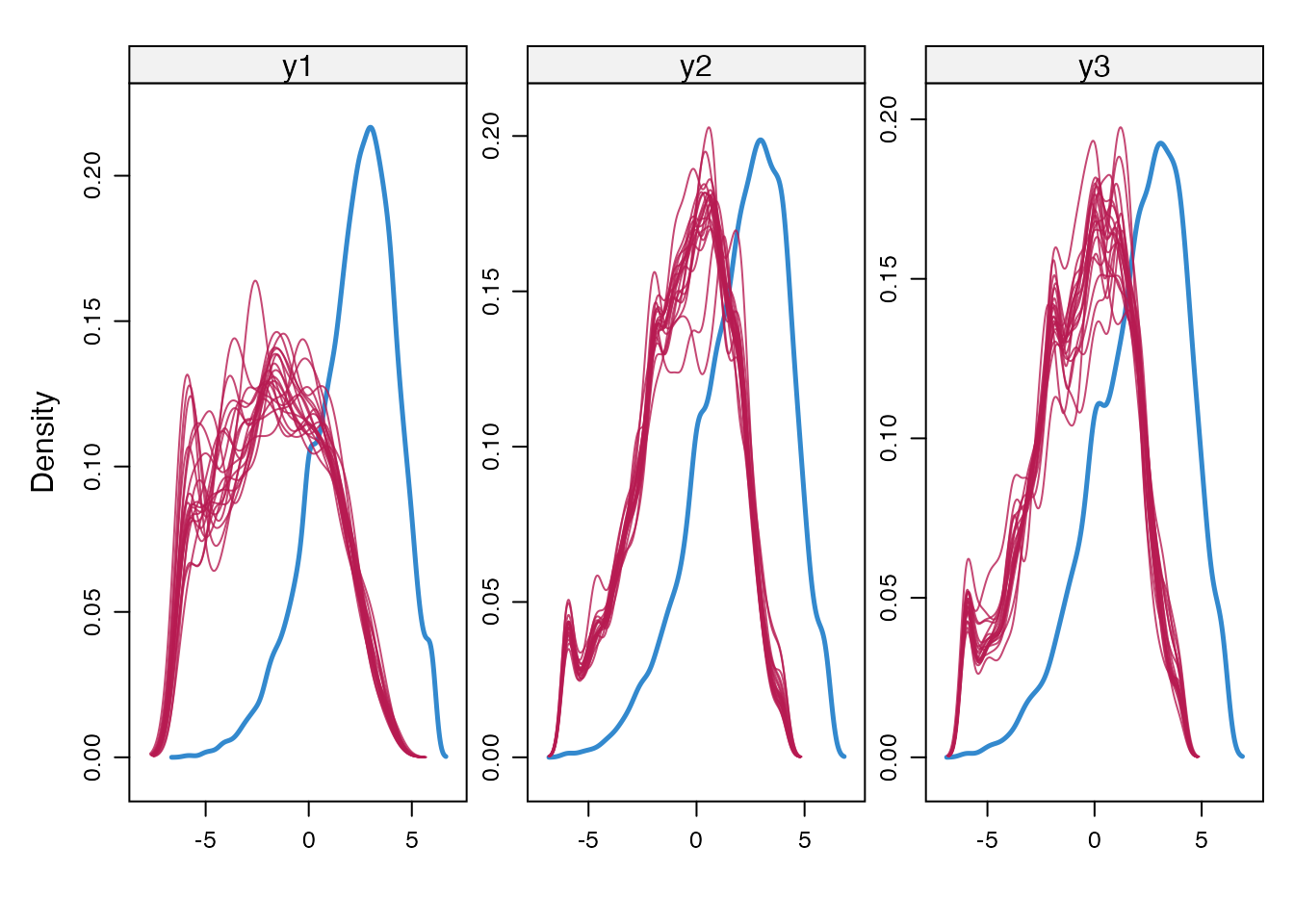
We also compare the imputed slopes for 14 participants, asuming delta 0 or -2.
#' Plot the slopes for 15 participants and the imputations
plot_imputed_slopes <- function(imp) {
tmp <- mice::complete(imp, action = "all")
n_subs <- 14
tmp2 <- lapply(tmp, function(d) head(d, n = n_subs))
tmp2 <- bind_rows(tmp2, .id = "imp")
tmp2$id <- rep(1:n_subs, m)
tmp3 <- pivot_longer(
tmp2,
c(y1, y2, y3),
names_to = "y_var", values_to = "y"
)
tmp3_sum <- tmp3 %>%
group_by(id, y_var) %>%
summarise(y = mean(y))
ggplot(tmp3, aes(y_var, y, group = interaction(id, imp))) +
geom_line(alpha = .5) +
geom_line(data = tmp3_sum, aes(group = id), color = "blue", size = 1.5) +
facet_wrap(~id, nrow = 2) +
ylim(c(-6, 6))
}
plot_imputed_slopes(imp_mar) + labs(title = "Delta = 0") +
plot_imputed_slopes(imp2) + labs(title = "Delta = -2") +
plot_layout(nrow = 2)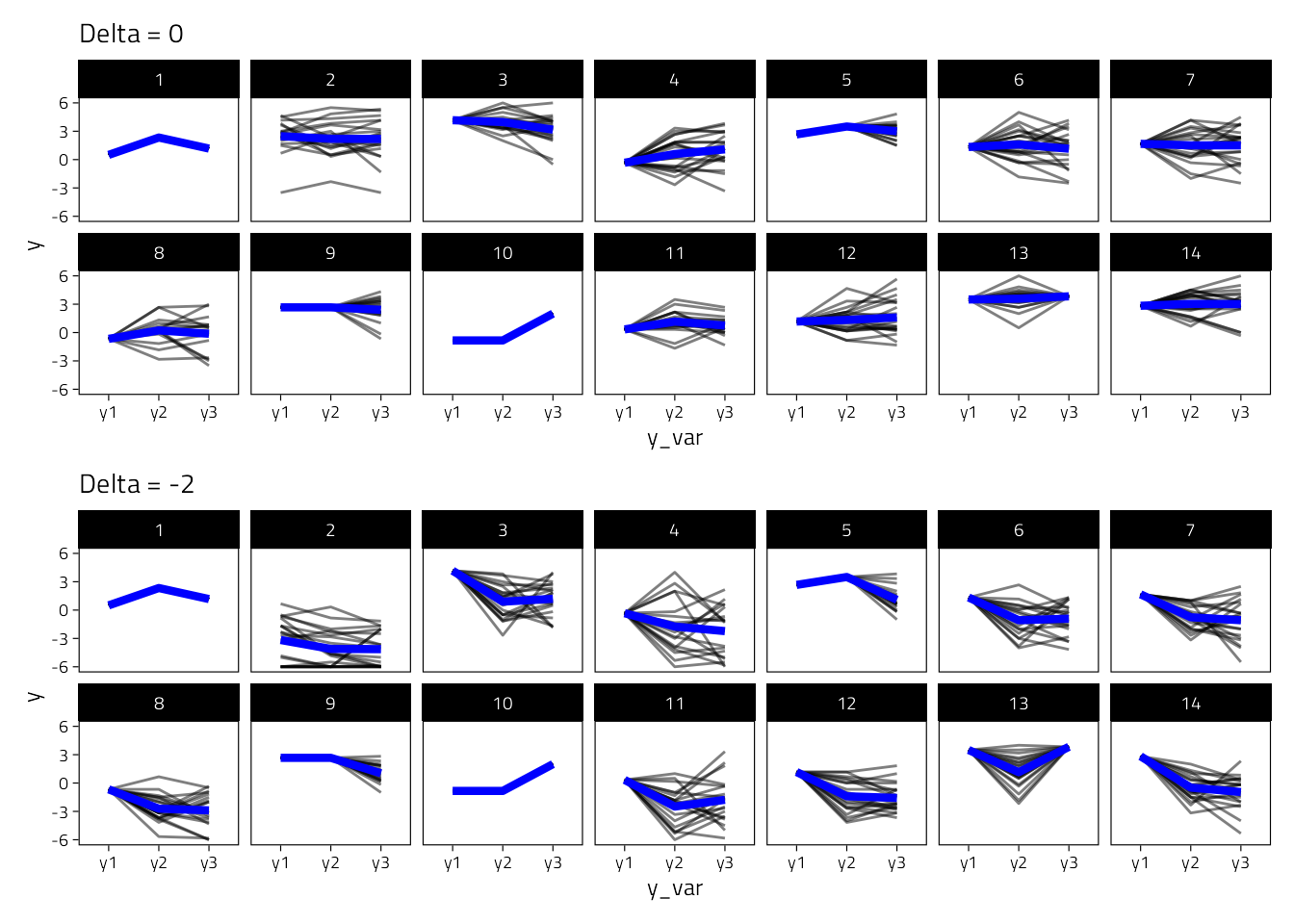
5.2 Analysis
For the analysis step we use the same lavaan model as for the main analysis.
We then fit the lavaan model to each imputed data set.
get_lavaan_pars <- function(x) {
bind_rows(
parameterestimates(x) %>%
mutate(Type = "Unstandardized"),
standardizedsolution(x) %>%
rename(est = est.std) %>%
mutate(Type = "Standardized")
) %>%
as_tibble() %>%
unite("Parameter", c(lhs, op, rhs), sep = " ", remove = FALSE) %>%
filter(Type == "Unstandardized", str_detect(Parameter, " ~ ")) %>%
filter(Parameter %in% c("wx2 ~ wx1", "wx2 ~ wy1", "wy2 ~ wy1", "wy2 ~ wx1"))
}
lavaan_mice_mnar <- function(data, delta = 0, m = 5) {
# use observed data only if m = 0
if (m > 0) {
imp <- mice_mnar_delta(data = data, delta = delta, m = m)
} else {
imp <- list(m = c(1))
}
# fit model to each imputed dataset
fit_multi_imp <- lapply(seq_len(imp$m), function(i) {
if (m > 0) {
d_tmp <- mice::complete(data = imp, action = i, include = FALSE)
} else {
d_tmp <- data
}
fit_riclpm_sep <- d_tmp %>%
group_by(Game) %>%
summarise(
fit = lavaan(
riclpm_constrained,
data = cur_data(),
missing = "ml",
meanstructure = TRUE,
int.ov.free = TRUE
) %>% list()
)
out <- fit_riclpm_sep %>%
mutate(pars = map(fit, get_lavaan_pars)) %>%
select(-fit) %>%
ungroup() %>%
unnest(pars)
out$imp <- i
out$delta <- delta
out
})
fit_multi_imp
}All lavaan models are then meta-analyzed
# Load cache if it exists
file_path <- here("Temp", "lavaan-MI.rds")
if (file.exists(file_path)) {
fit_mnar_imp <- read_rds(file = file_path)
} else {
# fit model without MI
fit_no_mi <- lavaan_mice_mnar(data = d, delta = "no MI", m = 0)
fit_mnar_imp <- lapply(
deltas,
function(delta) lavaan_mice_mnar(data = d, delta = delta, m = m)
)
fit_mnar_imp <- c(list(fit_no_mi), fit_mnar_imp)
write_rds(fit_mnar_imp, file = file_path)
}We perform the meta-analysis for each delta value and for the m (imputed) lavaan models.
#' Run MA with MICE lavaan objects
#'
#' @param data a list with results from the m imputations
run_MA_imp <- function(data, cluster, brms_empty) {
res <- lapply(data, run_MA, cluster = cluster, brms_empty = brms_empty)
res <- do.call(rbind, res)
all_imps <- res %>%
mutate(out = map(fit, get_ma_post)) %>%
mutate(
out2 = map(
out,
~ describe_posterior(.x, centrality = "mean", ci = 0.95) %>%
rename(Game = Parameter)
)
) %>%
select(-fit, -out) %>%
unnest(out2) %>%
select(-CI, -starts_with("ROPE")) %>%
group_by(Parameter, Game) %>%
mutate(imp = row_number()) %>%
as.data.frame()
pooled <- res %>%
group_by(Parameter) %>%
summarise(
fit = combine_models(mlist = fit, check_data = FALSE) %>% list()
)
pooled$delta <- as.character(data[[1]]$delta[1])
# only return posterior summary to save space
pooled <- pooled %>%
mutate(out = map(fit, get_ma_post)) %>%
mutate(
out2 = map(
out,
~ describe_posterior(.x, centrality = "mean", ci = 0.95) %>%
rename(Game = Parameter)
)
) %>%
select(-fit, -out) %>%
unnest(out2) %>%
select(-CI, -starts_with("ROPE")) %>%
as.data.frame()
list("all" = all_imps, "pooled" = pooled)
}
run_MA <- function(data, cluster, brms_empty) {
fit_ma <- data %>%
group_by(Parameter) %>%
mutate(i = cur_group_id()) %>%
partition(cluster) %>%
summarise(
fit = list(
update(
brms_empty,
newdata = cur_data(),
control = list(adapt_delta = .9999, max_treedepth = 15),
iter = ITER, warmup = WARMUP,
refresh = 0,
)
)
) %>%
collect()
fit_ma$delta <- data$delta[1]
fit_ma
}
# get posterior summaries
get_ma_post <- function(x) {
coef(x, summary = FALSE) %>%
.[["Game"]] %>%
.[, , 1] %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
cbind(fixef(x, summary = FALSE)) %>%
as_tibble()
}
# Save/load meta-analyses in one file
file_path <- here("Temp", "brms-MI-meta-analyses.rds")
if (file.exists(file_path)) {
fit_ma_imp <- read_rds(file = file_path)
} else {
# Meta-analyze the models fitted independently to games
d_ma <- fit_mnar_imp[[1]][[1]]
# Compile meta-analytic brms/Stan model
bf_ma <- bf(est | se(se) ~ 0 + Intercept + (0 + Intercept | Game))
fit_ma_empty <- brm(
bf_ma,
data = d_ma,
prior = prior(student_t(7, 0, 0.25), class = "sd", group = "Game") +
prior(normal(0, 0.5), class = "b"),
chains = 0,
control = list(adapt_delta = .999)
)
cluster <- new_cluster(4)
cluster_library(cluster, c("dplyr", "brms", "here", "stringr"))
cluster_copy(cluster, c("fit_ma_empty", "ITER", "WARMUP"))
fit_ma_imp <- lapply(
fit_mnar_imp,
function(data) run_MA_imp(data, cluster, fit_ma_empty)
)
rm(cluster)
write_rds(fit_ma_imp, file = file_path)
}
pooled <- lapply(fit_ma_imp, function(d) d$pooled) %>%
bind_rows() %>%
mutate(delta = factor(delta))
all <- lapply(fit_ma_imp, function(d) d$all) %>%
do.call(rbind, .)
rm(fit_ma_imp)Here we check so that the correct number of imputations were performed.
all %>%
group_by(delta, Parameter) %>%
summarise(n = n())## # A tibble: 24 × 3
## # Groups: delta [6]
## delta Parameter n
## <chr> <chr> <int>
## 1 -1 wx2 ~ wx1 160
## 2 -1 wx2 ~ wy1 160
## 3 -1 wy2 ~ wx1 160
## 4 -1 wy2 ~ wy1 160
## 5 -2 wx2 ~ wx1 160
## 6 -2 wx2 ~ wy1 160
## 7 -2 wy2 ~ wx1 160
## 8 -2 wy2 ~ wy1 160
## 9 0 wx2 ~ wx1 160
## 10 0 wx2 ~ wy1 160
## # … with 14 more rowsWe also take a look at some of the imputed coefficients.
all %>%
filter(Game == "Intercept", delta == -1) %>%
mutate(imp = factor(imp)) %>%
ggplot(
aes(Mean, imp)
) +
geom_point() +
geom_linerange(aes(xmin = CI_low, xmax = CI_high)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0) +
facet_wrap(~Parameter, scales = "free_x") +
labs(x = "Imputation", y = "Estimate")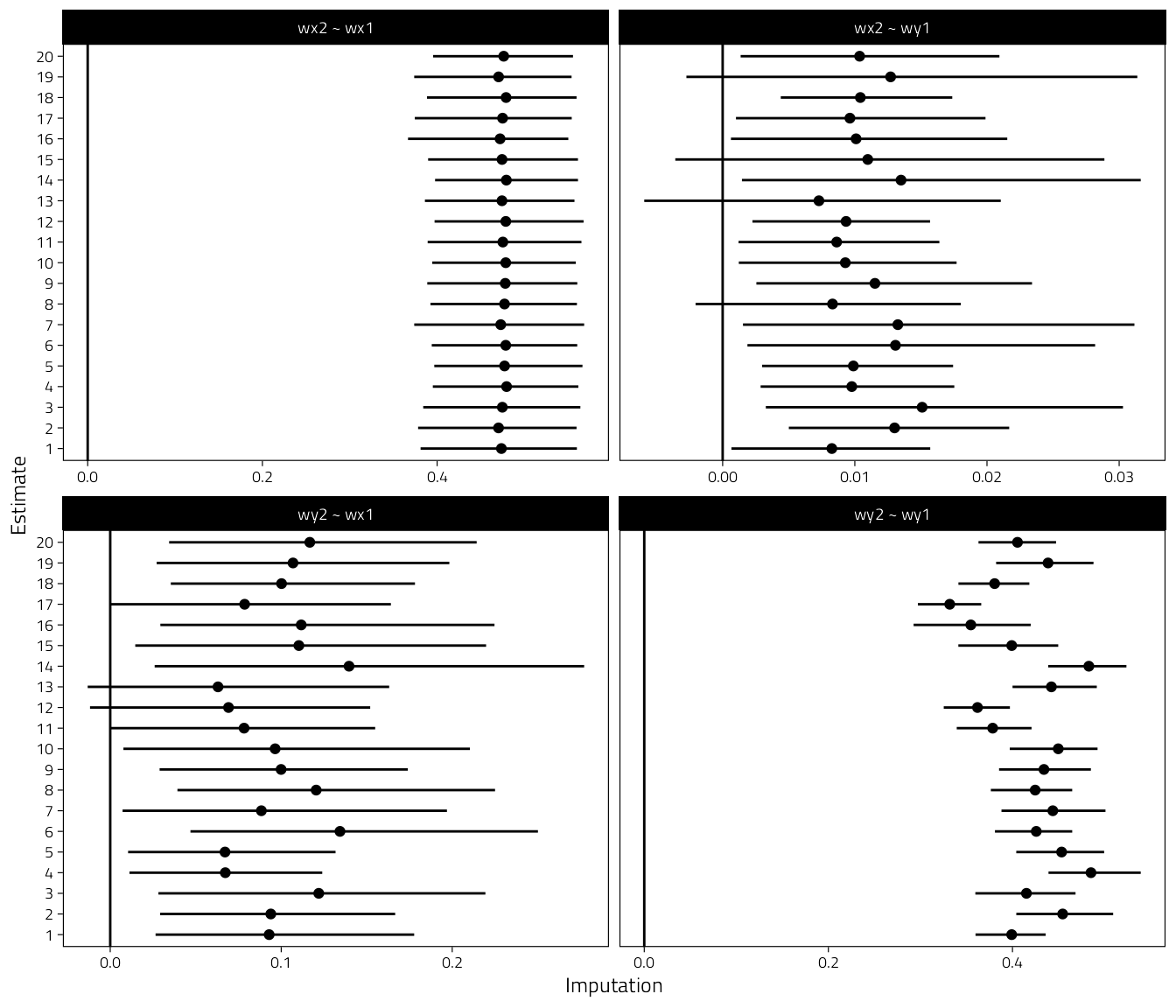
Figure 5.1: Results from the missing data sensivitity analysis. Coefficients plus 95% CIs for each imputation when delta = -1
5.3 Sensitivity plot
We plot all regression coefs, “wy2 ~ wx1” should be the most interesting one.
pooled %>%
tibble() %>%
mutate(Game = if_else(Game == "Intercept", "Average", Game)) %>%
mutate(Game = fct_rev(fct_relevel(Game, "Average"))) %>%
mutate(
delta = factor(
delta,
levels = c("-2", "-1", "0", "no MI", "1", "2")
)
) %>%
ggplot(
aes(Mean, delta, color = delta)
) +
geom_point() +
geom_linerange(aes(xmin = CI_low, xmax = CI_high)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
labs(y = "Delta adjustment", x = "Estimate") +
facet_grid(Game ~ Parameter, scales = "free")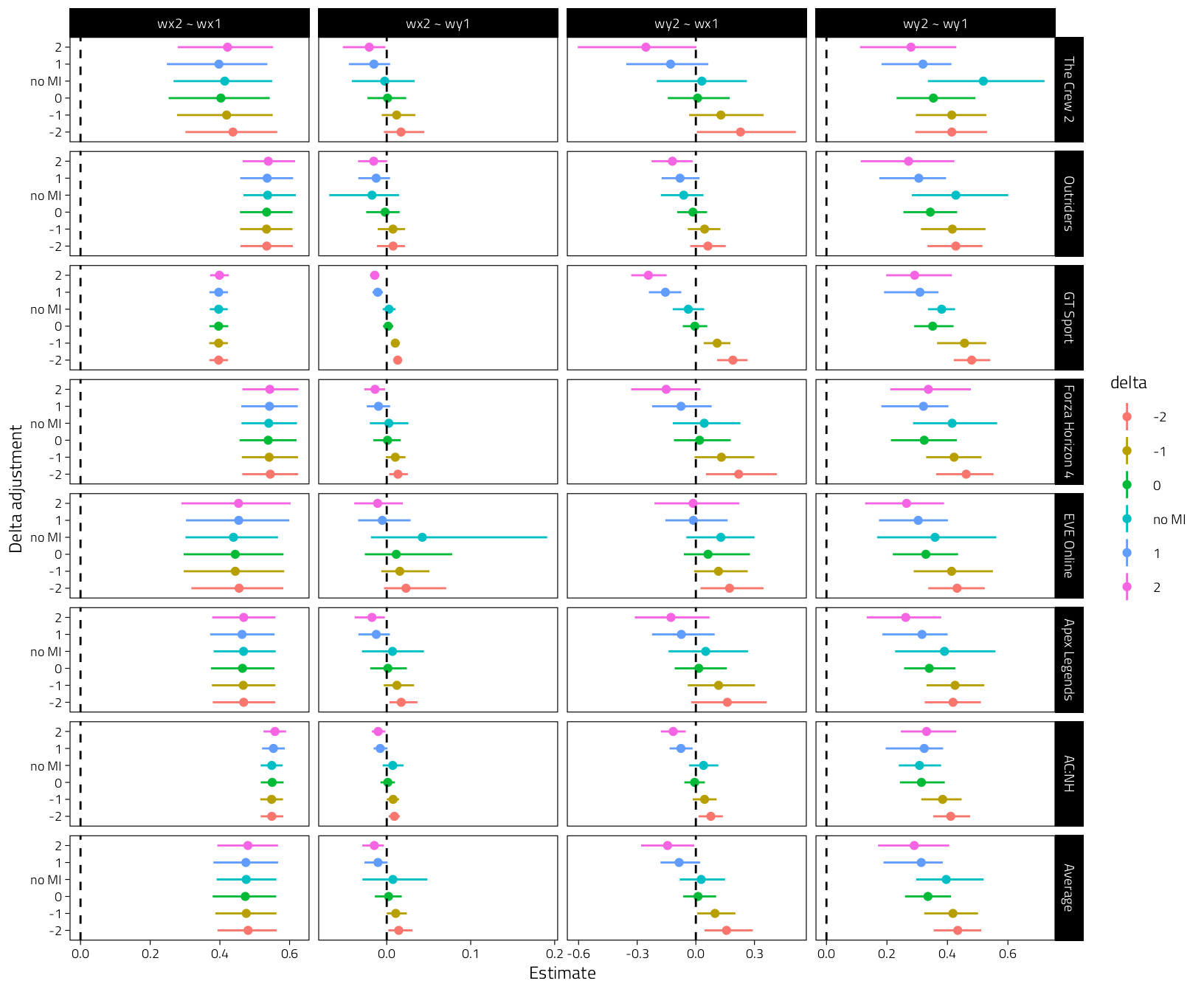
Figure 5.2: Coefficients plus 95% CIs for the pooled MI models